


Hearing Loss
Hearing loss refers to the fact that one or both ear organs are damaged in an unsatisfactory manner, and sound waves cannot be transmitted normally, resulting in a decrease in hearing ability. This problem is not only related to old age but can happen to people of any age.
The sound you hear is a sound wave that vibrates through the tympanic membrane through the outer ear guide and transmits the sound wave to the ossicles of the middle ear and then to the cochlea (the auditory organ). The nerve cells (hair cells) in the cochlea are stimulated to send signals to the auditory nerve and the brain, and the brain will distinguish and analyze the received signals as sounds. Once hair cells are damaged, they cannot regenerate, which affects hearing ability. To learn more, you can refer to the following chart:


Causes of hearing loss
The organs of the ear are small and delicate, and there are many reasons for hearing loss, the most common are:
- Congenital
- Old age
- The external ear canal is blocked or infected with earwax or foreign body
- The effects of otitis media or middle ear disease (including mumps, flu, Meniere’s disease)
- Affected by drugs, especially anti-cancer drugs and antibiotics
- Traumatic (including severe impact, swimming or diving) may cause rupture of the tympanic membrane, displacement or damage of the ossicles
- Excessive prolonged exposure to high-noise environments, including occupational deafness
Occupational deafness
Occupational deafness is a kind of neurological deafness and a common occupational disease. The main cause is the long-term work or activities in a high-noise environment. The noise passes through the shell, ear canal and eardrum of the outer ear, and then enters the middle ear and inner ear. For a long time to withstand high levels of noise will slowly destroy the nerve cell tissue (hair cells) of the inner ear. Once these cell tissues die, they cannot regenerate, leading to permanent damage, resulting in unsatisfactory deafness.
Hearing loss and hair cells

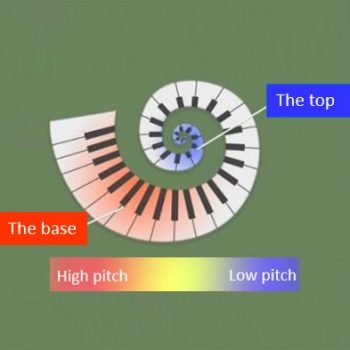
The human cochlea is shaped and structured like a snail shell. Inside it is actually densely packed with thousands of nerve cells called hair cells, which bear the great responsibility of perceiving sound. Hair cells will be reduced and damaged with age, traumatic diseases and high noise. The fewer hair cells, the worse the hearing ability.
Any sound, including human voice and environmental noise, contains different frequencies (that is, high, middle and low frequencies), and the hair cells of the cochlea are arranged from the base to the top. The base (entrance) of the hair cell is the high-frequency hair cell to the top (end) is the low-frequency hair cell, so under normal circumstances, the entrance (high-frequency) hair cell will be damaged and necrotic first. Most of the hearing loss is the loss of high frequency first, so the wife often complains that the husband does not listen to her, maybe the high frequency hair cells of the husband’s cochlea have been necrotic!
Hearing loss symptoms
As long as you pay attention, you can easily notice the following symptoms of hearing loss:
- Listening to others, accustomed to head sideways
- Often say “pardon me” in conversations
- Often ask the other party to repeat the conversation
- Can’t keep up with the content of the other person’s speech, especially the conversation of several people
- Under noisy background, it is difficult to understand the words of others or misunderstand the content of the conversation
- The TV volume or speak loudly
Consequences of hearing loss
In daily life, the decline in hearing ability not only brings inconveniences in daily life, but also seriously affects one’s uneasy state of mind:
- Due to low awareness, accidents are prone to occur outdoors and at home
- Older people will lack balance and fall easily
- Misunderstandings occur from time to time between words and affect family harmony
- It will accelerate the dementia and dementia of the elderly. The international authoritative medical journal (The Lancet)points out that the risk of dementia due to hearing loss is also greatly increased.
- Affects communication between people, prone to anxiety and depression. A study by the Chinese University of Hong Kong: Nearly 20% of the elderly with moderate or above hearing impairment have depression symptoms
- Children’s hearing loss affects their learning and speech ability
What to do with hearing loss?
As our hearing organ, if there is a problem with the ear, it will cause us a lot of inconvenience in life. If you have any questions, please consult professionals as soon as possible.
Whether it is congenital, old age, disease, or permanent hearing loss caused by the treatment of anaphylaxis, it is basically irreversible. You need to find professional evaluation and fitting suitable auxiliary equipment to improve your quality of life. The new generation of 5G high-efficiency noise reduction hearing aid products can effectively reduce the noise by 90%, making the voice clear. According to the clinical evidence of the University of Hong Kong, 91% of users feel that it is better than the previous ones.
If you suspect that there is a pathological problem in the ear, you need to be checked by an otolaryngologist. The doctor will provide appropriate treatment based on the actual condition of the ear.
How to prevent hearing loss
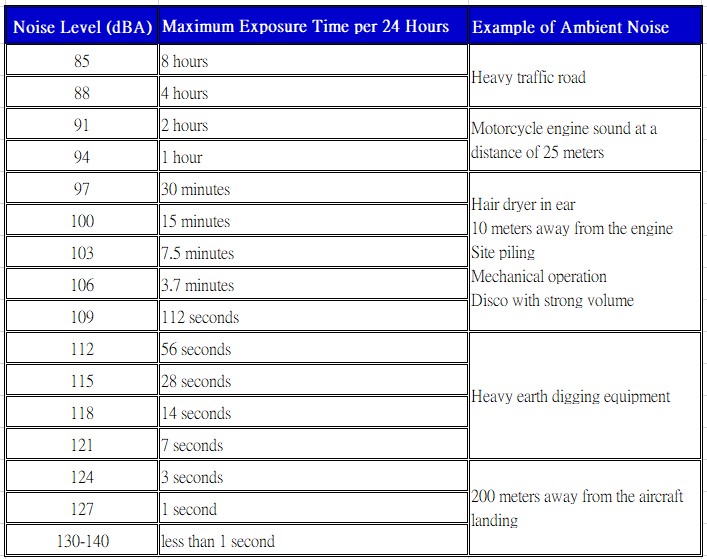
Hearing ability declines tend to increase. Young people use headphones for a long time to listen to music, and exposure to high volume environments will lead to hearing ability decline. The following chart shows the maximum exposure time per 24 hours. Paying attention to the time and volume of daily noise reception can effectively prevent hearing loss.




